Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) solutions aim to bring us closer to the Zero Trust security model by reducing implicit trust zones. But do they live up to their name? In this article, we’ll explore where ZTNA falls short of the Zero Trust principle and how organizations can bridge the gap.
The Reality of Trust Zones in ZTNA
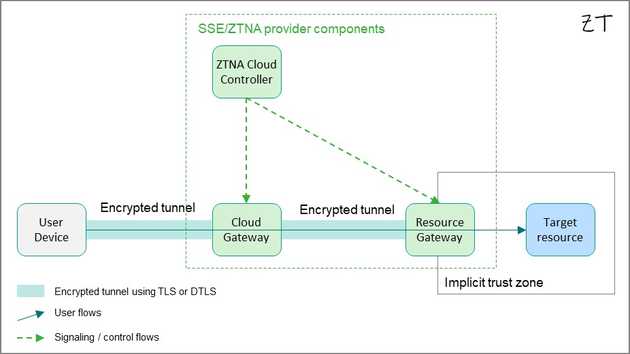
ZTNA solutions aim to reduce implicit trust zones by confining them to the space between the resource gateway-also referred to as the connector or publisher by some vendors- and the resource itself. While this approach aligns with network segmentation, it inherently deviates from Zero Trust principles by allowing an implicit trust relationship between the resource gateway and the resource.
Deploying a resource gateway to each resource might seem like a solution, but it’s impractical. Doing so would require a resource gateway for every server, virtual machine, or container leading to significant scaling challenges and increased costs, making it an inefficient strategy for achieving true Zero Trust.
The Problem of Expanding Trust Zones
To reduce complexity and costs, organizations often deploy a single resource gateway or a pair to manage multiple resources. As resources are added, the trust zone grows, creating a larger area of implicit trust. This expansion moves further away from Zero Trust principles and introduces new vulnerabilities. ZTNA, while reducing trust zones, does not inherently achieve Zero Trust objectives. Organizations must continually adjust and refine their implementation to minimize trust zones and maintain security.
The Challenge of Securing Resource gateways
Even the smallest trust zone depends on the security of the resource gateway itself. Critical questions include: • How is the resource gateway protected and hardened? • How can organizations reduce risks related to resource gateway vulnerability exploits, rogue, or unauthorized access? Unfortunately, many ZTNA solutions treat resource gateways as a “black box," offering limited visibility or control to organizations. This lack of transparency can hinder efforts to build a truly robust Zero Trust architecture.
Moving Toward True Zero Trust
To address these limitations, organizations should take the following steps:
- Continuously Evaluate Trust Zones: Regularly assess and adjust trust zones to align with Zero Trust principles.
- Choose Transparent Solutions: Opt for ZTNA solutions that offer full visibility and control over resource gateways.
- Implement Additional Safeguards: Monitor resource gateways for potential threats and ensure they are properly hardened.
- Adopt Modern Micro-Segmentation: Complement ZTNA with micro-segmentation to limit lateral movement within networks.
ZTNA and SSE solutions provide a strong foundation, but achieving true Zero Trust requires more. Organizations must invest in thoughtful design, continuous refinement, and proactive risk management. These solutions are not “set-and-forget” tools; they demand consistent effort to remain effective.
Need Expert Guidance?
Building a Zero-Trust architecture that fits your organization’s unique needs can be challenging. With my expertise in SSE and Zero Trust, I can help you select the right solutions and design a security strategy tailored to your goals. Reach out today, and let’s take the next step toward securing your infrastructure.